Diseases of the musculoskeletal system in almost all cases are accompanied by dysfunction of its organs, which causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient.
An important symptom of pathologies of the musculoskeletal frame is pain. Joint injuries are particularly unpleasant.
The hip is the largest of them. Pain in case of defeat can be localized both around it, and transmit it to various anatomical structures: to the organs of the small pelvis, lower back or thigh.
General classification of causes
The etiology of hip pain is varied.
In medicine, the following causes of arthralgia are conditionally distinguished:
- Inflammatory and infectious processes inside the joint and its surrounding tissues.
- Degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
- Injuries.
- Bone and soft tissue tumors.
There are other specific causes of arthralgia:
- Piriformis syndrome. Associated with its prolonged spasm.
- Femoral head necrosis (GBC). Most often, it is a complication of another TBS pathology.
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. She has GBC osteochondropathy.
- Dissection of osteochondrosis. In different sources it can be called Koenig's disease.
- Diabetic osteoarthropathy. Complication of diabetes.
- Pseudogout. Also chondrocalcinosis.
- Intermittent rheumatoid arthritis is an overproduction of synovial fluid.
- Synovial chondromatosis (Lotsch syndrome).
Also, the leg in the region of the hip joint in pregnant women often hurts.
During this period, complex hormonal changes occur, the growing uterus displaces neighboring organs and strains the ligamentous apparatus of the hip joint. In addition, weight gain increases the load on the legs. If dietary recommendations are not followed, a pregnant woman can develop a lack of calcium, because of this mineral imbalance, the structure of bones and joints is disturbed.
Causes of pain
The prevalence of arthralgia increases with age.In children, symptoms of the disease of the TSS (hip joint) occur with a frequency of not more than 10%, and in the elderly - from 50%. Most women suffer from this pathology. This is due to age-related hormonal changes after menopause.

Why does the hip joint hurt? There is no definitive answer to this question, as the list of reasons is quite long.
The main factors provoking arthralgia in the hip joint:
- Pathological process inside the musculo-ligamentous apparatus. Most often it is a consequence of a direct mechanical action: a bruise of the joint followed by inflammation of its components.
- Anatomical changes in the joint. They can be congenital or post-traumatic (dislocations, fractures).
- Pathology of other systems. Inflammation of the organs of the MT (small pelvis) can spread to the bones of the pelvis. Neurological disorders are manifested by pain of any localization. Metabolic disorders cause a mineral imbalance. The bone-ligament connection weakens, the risk of injury increases.
Inflammatory and infectious processes in the joints and surrounding tissues
The most common cause of arthralgia, regardless of localization, is suppuration of the musculoskeletal joint.
Inflammation of the hip joint is classified into:
- Primary. It is formed with direct penetration of pathogens into the joint: a blow with a sharp or blunt object with the formation of a wound.
- Secondary. TBS infection occurs from a distant inflammatory site: by contact or by the hematogenous route.
Arthritis TSS
Occurs mainly in elderly patients.Aching pain in the hip joint, aggravated by walking, radiates to the groin, perineum and thigh. It is difficult for the patient to get up from a chair or climb stairs without help. Discomfort worse in the morning.
Treatment consists of taking anti-inflammatories and introducing glucocorticoids into the intra-articular bursa. If necessary, its cavity is drained.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
It is a chronic systemic connective tissue disease similar to arthritis.The essence of this pathological process is inflammation of the synovium, cartilage and joint capsule. The reason is a malfunction of the immune system. Characterized by polyarthralgia, stiffness of movement in the morning, high fever is possible.
The shoulder and hip joints are extremely rarely affected, the pain appears only at a late stage of RA, a few years after the onset of the disease.
Acute septic arthritis
It is an infectious childhood disease, 70% of cases occur in babies under 4 years old. The causative agent is usually Staphylococcus aureus. The child refuses to walk because of severe sharp pains in the hip joint and groin when moving. Characterized by high fever and increased excitability.
Treatment includes removal of the effusion from the joint cavity and antibiotic therapy.
The risk of developing osteomyelitis and sepsis is high.
Tuberculous coxitis or arthritis
Most often, pediatricians are faced with this disease. In young children, the immune system is poorly developed, which leads to the possibility of infection.
This disease is characterized by slow progression. Initially, the child gets tired very quickly, his activity decreases, he stops running. Gradually, atrophy of the thigh muscles occurs. Movements are hampered. Pain in the hip joint in a child acquires an intense aching character, the limb becomes longer than a healthy limb.
If the pus melts the synovial membrane, the exudate spreads along the muscles and tendons, forming phlegmons and fistulas.
In the absence of complications, conservative treatment is carried out.
Tendovaginitis in the region of the hip joint
This pathology is an inflammation of the tendon of the muscle and its vagina. Caused by prolonged overuse or leg injury.
The main complaints: the femoral joint hurts when moving, the lesion swells, changes its gait - lameness becomes noticeable.
Treatment - drugs: anti-inflammatories, intra-articular injections of corticosteroids.
Bursitis
Of all the synovial pockets, the bursa of the acetabulum is most often inflamed.It partially covers the femur. With hip bursitis, the pain radiates to the thigh and buttock area. The patient cannot lie down on the affected side: the pressure in the synovial sac increases and the pain intensifies.
If there are no complications with bursitis, treatment consists of unloading the lower limb with a cane or crutch.
Medications: Analgesics and corticosteroids.
Idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis
This is a chronic inflammation of the spine and elements of the sacroiliac joints.
The disease is dangerous for its complications that reduce the standard of living and lead to disability.
If you find such a problem, you should immediately contact a specialist for the appointment of the appropriate treatment.
The etiology is not fully elucidated. Modern medicine suggests that the main cause is hereditary predisposition. Most often, people under 30 get sick.
Symptoms of idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis:
- Increased body temperature, fever.
- Intoxication syndrome: general malaise, weakness, lack of appetite, weight loss, sleep disturbances.
- Constant dull pain in the hip joint, as well as in the sacrum and buttocks, spreading along the back of the thigh. Generally bilateral, at night their intensity increases.
- Limited mobility in the lower back and hips. This symptom gradually moves to overlying sections of the spine along the entire back, including the neck. As a result, the patient assumes a forced "petitioner's pose".
Rehabilitation therapy is based on special physiotherapy exercises for joint development.
Medications: NSAIDs to relieve pain and inflammation, corticosteroids.
Tendonitis
Athletes or people whose work is associated with heavy physical labor are prone to inflammation of the tendons. Characteristic of the manifestation: aching pain in the hip joint occurs with a large load. At rest, discomfort is usually not observed.
It is recommended to reduce the load on the leg, in advanced cases - bed rest.
Drug treatment: NSAIDs, topical analgesic gels, glucocorticoids, chondroprotectors.
Syphilis
In the advanced stage of the disease, bones and joints are affected. Gum formation is characteristic. Their excessive pathological mineralization occurs. TSS is extremely rare.
Gum - a knot in the tissues, formed during advanced syphilis, destroying the surrounding tissues. The process ends with the formation of rough scars.
Treatment is ineffective, the risk of developing complications in the form of osteomyelitis is high.
Fungal arthritis of the hip
It occurs as a result of prolonged use of antibiotics and pathologies of the immune system.
People with HIV infection or AIDS are particularly susceptible to fungal arthritis.
Pain in the joint is constantly present, has a painful character.
Fungal lesions of the bones are characterized by a tendency to the formation of fistulas, the duration and difficulty of treatment.
Therapy: systemic antimycotics.
According to indications, surgical intervention is performed.
Bone and soft tissue tumors
Oncological diseases of the hip joint can be metastases of cancer from a distant organ or occur independently.
- Benign tumors of bone tissue - osteomas.
The formation foreign to the body grows, compressing the nerves and blood vessels. The clinic is similar to piriformis syndrome.
- Malignant bone tumors - osteosarcomas.
The neoplasm rapidly enlarges, necroses and decays, spreading metastases throughout the body.The pain in the hip joints at night is unbearable, they do not stop even after taking NSAIDs or trying to anesthetize.
- Mesenchymal tumors are formed from soft tissue. Benign ones rarely reproduce and do not metastasize. According to the aggressiveness of the malignant cells, the intensity of the pain is variable.
Degenerative diseases of the joint
Coxarthrosis
Arthrosis of the hip is a chronic disease characterized by a change in the integrity of the articular surfaces, due to a violation of metabolic processes. It develops very slowly, over several years. Initially, cartilage tissue is affected, then bone tissue, followed by varus deformity of the joint and limb. Occurs at age 40.
Symptoms:
- The hip joint hurts only when walking.
- Stiffness of movements in the TBS.
- As the process progresses, a shortening of the limb length is observed.
- Weakness and atrophy of muscle mass.
- Lameness.
- As you walk, a creak is heard.
- With a bilateral lesion, a "duck walk" occurs - transferring from one leg to the other.
Medications: NSAIDs, vasodilators, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, injections of hormonal drugs into the joint cavity.
Local effects: ointments, lotions, compresses.
At the last stage of the disease, surgical intervention is being carried out.
Osteochondrosis
Degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs damage the surrounding tissues.
Symptoms:
- Pain in the lower back radiating to the hip joint and thigh.
- It's sudden, sharp and clean. It starts in the lumbar region and the buttocks, goes down the back of the leg.
- Unilateral localization of pain is more common.
- The patient takes a forced position - lying on a healthy side.
- Probably decreased sensitivity of the skin of the leg.
The treatment is complex. Anti-inflammatories and analgesics, moderate physical activity (swimming), physiotherapy after relief of the most acute phenomena.
In case of pronounced pain, it is recommended to make an anesthetic block.
injuries
Wound
Pain of moderate intensity is characteristic, during active movements its intensity increases. The first time after an injury to the hip joint, a lameness appears, which quickly passes.
At rest, the symptoms disappear.
In order to quickly get rid of pain in the event of an injury to the pelvic joint, it is necessary to apply cold to the site of injury: an ice pack or a frozen product.
hip dislocation
Perhaps:
- Congenital. It is the result of unsuccessful childbirth or pathologies of intrauterine development. The child has uneven gluteal folds and shortening of the limb, possibly a pinched nerve, manifested by convulsions. If the dislocation is not corrected in early childhood, the child may become disabled later.
- Traumatic. Signs: severe, sharp pain, complete cessation of joint function, massive edema and extensive hematoma appear above the damaged area. Getting up from a chair or bed becomes impossible for the patient without assistance.
In the event of a dislocated hip, you must immediately go to the emergency room or the hospital.
broken bones
The hip joint is formed by strong strong bones.
The most common diagnosis in this subgroup is a fracture of the surgical neck of the femur. It is put mainly to women after 60 years.
The cause of such damage is a fall or impact in the area of the TBS.
The strongest pain is felt, the hip joint pulls and abscess, movement is almost impossible. The upper thigh swells, an extensive hematoma appears. The injured leg is shortened, the patient limps. When moving, a characteristic click is heard.
When a fracture occurs, the surrounding tissues are damaged, which is accompanied by a burning sensation. In the absence of treatment, an inflammatory process can begin here. If the nerve is pinched, you may feel a numbness in your thigh.
The treatment is complex: surgical and medical.
Specific causes of arthralgia
Piriformis syndrome
With the localization of pathological processes in the region of the hip joint, the surrounding tissues are also affected. A long-term spastic piriformis muscle compresses the sciatic nerve and its vessels, causing a number of symptoms:
- Pain in the leg in the region of the hip joint. It goes to the buttocks and the lumbosacral joint.
- Increased discomfort when leaning on the affected leg.
- Compression of the piriformis muscle.
- Sudden "lumbago" pain along the nerve.
Etiology: infectious and inflammatory lesions and diseases of the pelvic organs, vertebrogenic pathologies, muscle overtraining, long-term preservation of non-physiological posture.
Medicines: NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, analgesics, blood circulation improvers, glucocorticoids.
After the disappearance of acute phenomena, rehabilitation measures can be prescribed: physiotherapy, massage, acupuncture.
Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
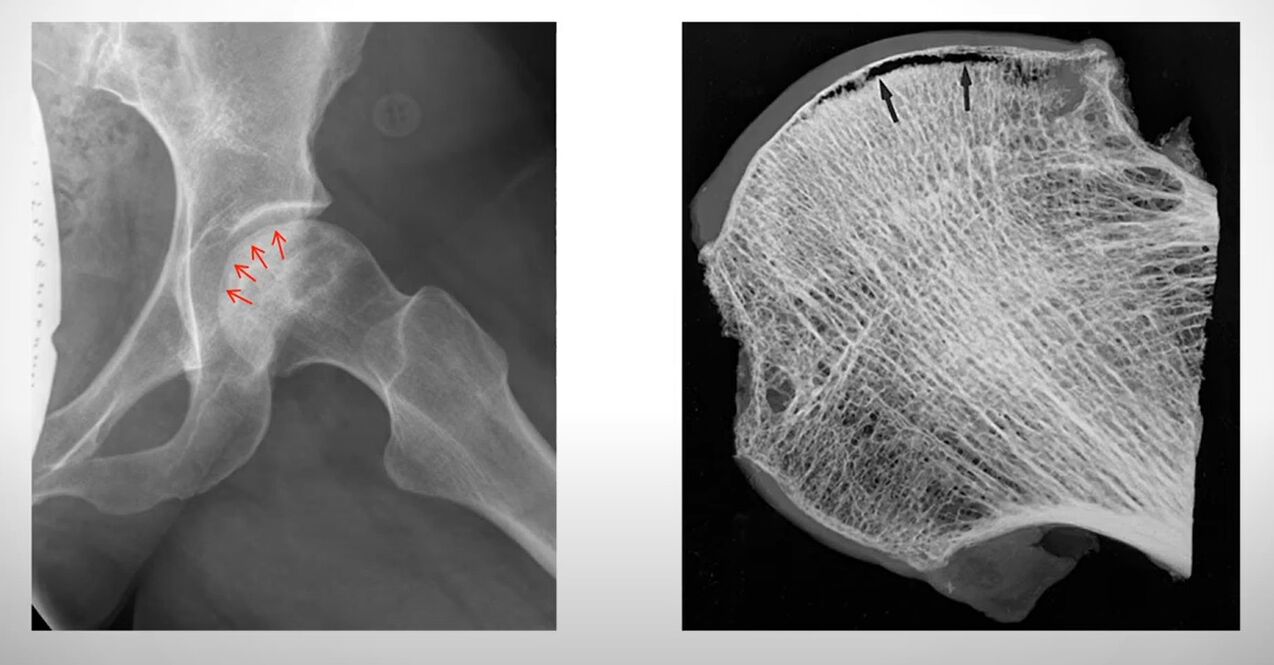
The vast majority occur in young men. The etiology of the disease is ischemia of the upper thigh. With insufficient blood supply to the tissues, their lack of oxygen occurs and their necrosis (necrosis) begins.
Clinical picture: the hip joint hurts and gives to the leg and perineum. It is not possible to rely on the injured leg. After a few days, the nerve endings melt and the pain subsides. This is a terrible sign! With the necrosis of the deep layers of the bone, the risk of rapid development of osteomyelitis and sepsis is high.
Treatment is based on surgery and drug therapy.
Koenig's disease
Osteochondritis dissecans - exfoliation of a small necrotic cartilaginous area of the bone and its protrusion into the joint cavity.
It is a rare disease. Typical for men 15 to 35 years old.
Patients complain of mild pain in the hip joint. The joint "sticks" when moving.
The treatment is conservative (duration 10-18 months) and surgical. During surgery, the exfoliated masses are removed, the congruence (comparability) of the articular surfaces is restored.
Diabetic osteoarthropathy
Violation of glucose metabolism leads to circulatory disorders and innervation of all organs. Changes in the hip joint are more often unilateral: on the right, they occur more often than on the left. The immune response is reduced, making it easier for the body to infect.
Clinical picture:
- Swelling of the joint.
- The skin covering it is cold to the touch.
There is no pain syndrome in diabetic osteoarthropathy!
Treatment consists of careful blood glucose monitoring and prompt administration of insulin.
pseudogout
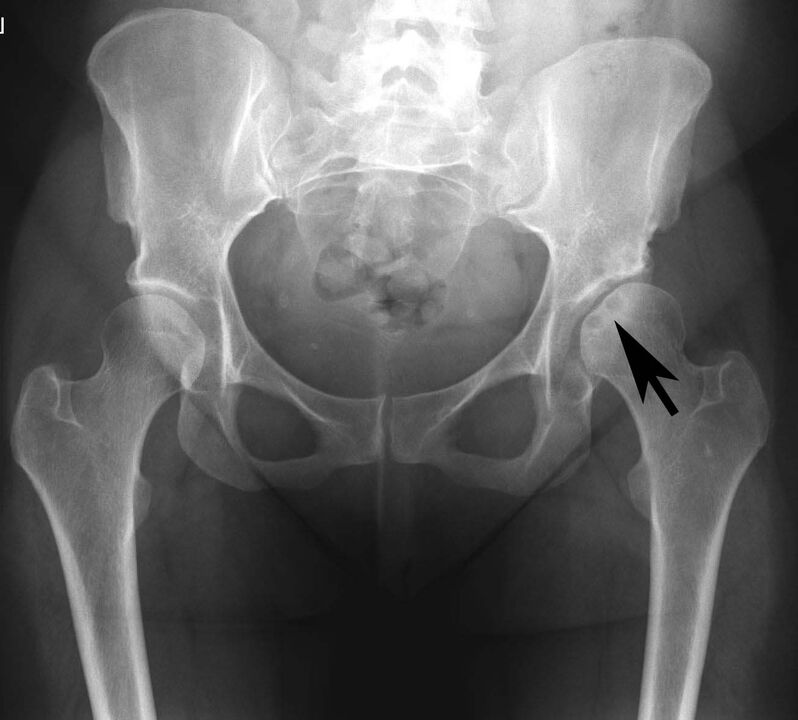
This pathology is the deposition of calcium salts in the articular cartilage.
Doctors associate it with endocrine pathologies: hyperparathyroidism, diabetes, gout, etc.
Symptoms:
- Beginning with sharp pain in the hip joint.
Several types of calcium salts are known. With some of them (pyrophosphates) there is no pain.
- Movement is limited there, abduction of the leg to the side is difficult.
- Edema and hyperemia are characteristic.
- Increased body temperature and fever.
To date, there is no specific treatment. An acute attack is stopped by intra-articular administration of corticosteroids and NSAIDs.
Intermittent hydrarthrosis
It is a chronic disease, which is manifested by episodes of increased production of synovial fluid. prone to frequent relapses.
It is diagnosed mainly in women between the ages of 20 and 40.
The etiology is unknown. There are two theories about the occurrence of this disease: associated with injuries and caused by endocrine disorders.
The joint increases in size, becomes stiff.
Attacks pass on their own in 3-5 days.
Medical treatment is ineffective. Relapses occur even after surgery.
Synovial chondromatosis
This benign metaplastic disease is the replacement of synovial collagen by cartilage. The structure of the articular surface changes, as well as its properties.
The risk of contracting chondromatosis is much higher in men, mainly in middle and old age.
The etiology is unclear.
There is local swelling, limited function of the joint, creaking during work, arthralgia.
The treatment is only surgical.
Hip pain in children and adolescents
epiphyseolysis
This pathology is more typical in children during puberty (from 11 to 16 years old). At this time there is a sharp increase in growth. Due to the low growth area, the HBA slips on the neck, causing discomfort in the hip joint.
The child feels pain in the thigh, passing into the groin and knee. Lameness is noted, but dependence on the limb is maintained.
The disorder is surgically corrected. You should start treatment as soon as possible. Otherwise, slippage of the HBA can provoke the development of arthrosis and inflammation of the joints.
Dysplasia
It is an excessive formation of connective tissue which can replace bone elements. As a result, solid anatomical structures become plastic, flexible. Ligaments, menisci and tendons weaken. An unstable hip forms, which is distinguished by frequent dislocations.
Dysplasia is an inherited condition that usually occurs in infants between 3 months and 1 year old. Orthopedists can easily cope with the correction of the adjustment of the legs.
The latent form may appear in adolescence.
If you notice manifestations of clubfoot or deformity of the foot in a child, you should promptly go to the hospital for an examination of the musculoskeletal system of the baby!
The later dysplasia is detected, the more problematic its treatment.
Osteochondropathy
This group of diseases includes damage to bone and cartilage tissues, in which the most stressed areas undergo aseptic necrosis.
Etiology: genetic predispositions, hormonal imbalances and infections can cause this pathology.
In 30% of cases, the hip joint is affected. These are mainly childhood diseases that are common in adolescents during the growth spurt.
An adult should at the initial stage determine the localization and nature of the pain, contact a pediatrician and obtain the necessary information to prevent the development of complications.
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
The syndrome is characterized by HBK necrosis in children under 15 years of age. The right hip joint is most commonly affected.
The cause of the pathological condition is a violation of blood circulation in the upper leg with the addition of cartilage tissue to the process.
Clinical picture:
- At first, the head of the femur hurts. With the progression of necrosis, arthralgia suddenly disappears. This indicates the death of the receptors of sensitive organs.
- Change of gait - the child begins to limp.
- Travel within TBS is restricted.
- Usually unilateral.
Complications: dislocation, coxarthrosis, lower limb deformity, muscle atrophy.
Diagnostic measures
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor should carefully study the complaints, anamnesis and conduct an examination.
In case of hip joint disease, the following studies are necessary:
- Laboratory blood tests (with inflammation, the ESR increases and leukocytosis is noted).
- Standard x-ray of the joint in two or more projections.
- MRI with or without contrast.
- MSCT. It is used to check for the presence of sarcoma.
- Osteoscintigraphy. radionuclide method. The most common and informative type of bone tissue examination.
- Ultrasound of the hip joint.
- Densitometry. Needed to determine bone density and strength.
If the patient cannot sit or stand and there is no need for pain relief, he is immediately sent to the hospital for further surgical treatment.
When to see a doctor urgently
- When there is a sharp pain when moving in the hip joint.
- If it is impossible to support the affected leg.
- Detection of edema of the lumbar and femoral region.
- Redness or bruising in the affected area.
There are traditional ways to relieve pain in the pelvic joint. Relying on these tips for a quick recovery is not worth it. Without a thorough diagnosis, it is impossible to determine the cause of arthralgia, and self-medication will lead to the development of complications.































